Advertisement
Artificial intelligence has evolved far beyond data processing and decision trees. Today, it shapes stories, simulates emotions, creates hyperrealistic images, and can even mimic a person’s voice or face in real time. The rise of these capabilities is transforming how people perceive truth, fiction, and everything in between. What once clearly separated the real from the imagined is now increasingly murky, thanks to the immersive power of AI-generated content.
This post will explore 8 key ways artificial intelligence is blurring the line between reality and fantasy — and why it matters more than ever.
AI-generated deepfakes have reached a level where they can be nearly impossible to distinguish from real videos. Using neural networks and deep learning, these tools can superimpose someone’s face onto another body, replicate speech patterns, and mimic emotions.
While some uses are harmless like creating movie scenes or funny content — the darker side includes political misinformation, identity theft, and public deception. Deepfakes are perhaps the clearest example of how AI-generated content can be both impressive and deeply misleading.
From video games to animated films, AI is now being used to create lifelike characters who respond to players or viewers dynamically. These characters don't just follow pre-written scripts; they adapt in real time, hold conversations, and can even express emotion using machine learning algorithms.
As AI characters become more intelligent and expressive, the line between human interaction and digital simulation gets blurrier. Players can form emotional bonds with avatars, often forgetting they’re interacting with code, not consciousness.
Voice cloning has surged with AI’s advancement in speech synthesis. Tools can now replicate the sound, tone, and cadence of any voice with just a few minutes of audio data. The result? It’s possible to make anyone say anything convincingly.
From voiceovers to podcast production, this has changed content creation. But it’s also led to ethical challenges, like impersonation scams and the creation of false narratives, which call into question what can really be trusted in audio media.

AI isn’t just processing commands; it’s learning to “feel.” While these systems don’t actually experience emotions, they can analyze human input to simulate emotional responses.
These emotionally intelligent bots are used in therapy apps, customer service, and even companionship platforms. Their ability to mirror empathy and care tricks the human brain into forming attachments. This psychological phenomenon of anthropomorphism is making AI feel more like "someone" than "something."
Tools like DALL·E, Midjourney, and text generators can now create artwork, poetry, or full novels. These outputs may seem inspired or even emotionally moving despite coming from algorithms trained on vast datasets.
It challenges traditional ideas about creativity. If a poem moves you or a painting stirs emotion, does it matter if a person or a machine created it? This philosophical tension is another way AI confuses what is authentic and what is synthetic.
On social media, not all influencers are real. Some, like Lil Miquela, are entirely AI-generated personas with millions of followers. These virtual influencers post, collaborate with brands, and engage in public discourse — just like real humans.
Followers engage with them as if they’re real despite knowing they’re not. This cognitive dissonance reveals how willing people are to accept fantasy as reality if it’s engaging or entertaining enough. It highlights a shifting social dynamic where emotional connection can override the need for authenticity.
With augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) merging with AI, users can now experience environments that blend real-world input with machine-generated enhancements. AI adjusts these immersive spaces in real time based on behavior, emotion, and context.
Think of walking through a virtual city where the weather matches your mood or an AI tour guide who knows your interests. These kinds of intelligent virtual worlds mix fiction with sensory realism so seamlessly that users may temporarily forget they’re inside a simulation.
Everyday users can now transform their appearance in real time using AI filters on platforms like Instagram, TikTok, or Snapchat. These filters don’t just smooth skin; they can change bone structure, eye shape, or even ethnicity with a few taps. The result is a version of the self that may be more fantasy than reality.
It creates a disconnect between digital personas and real-world identities, leading to new psychological phenomena like “Snapchat dysmorphia,” where people want to look like their filtered selves. AI here doesn't just enhance; it distorts.
Some AI chatbots are explicitly designed for emotional or romantic interaction. These bots learn user preferences, simulate affection, and provide companionship in a way that feels eerily real. People have been known to form genuine emotional bonds and even fall in love with AI personas.
Although these relationships are one-sided, the illusion of mutual connection is powerful. In simulating love or companionship, AI redefines what relationships can look like even when only one party truly exists.

In cutting-edge therapy and PTSD treatment, AI is being used to create simulated environments that replicate real memories — or even fabricate new, positive ones. These environments feel authentic enough to affect emotions, helping users confront trauma or anxiety in a controlled setting.
But when memories are recreated or invented in lifelike detail, the mind may struggle to separate the past from simulation. It introduces new challenges in memory integrity and emotional processing.
Artificial intelligence is reshaping our perception of the real world. Through voice cloning, virtual influencers, deepfakes, and emotionally intelligent bots, the line between what’s real and what’s imagined has never been thinner.
This blurring effect isn’t inherently bad — it offers exciting possibilities in art, therapy, education, and entertainment. But without ethical boundaries and public awareness, it also opens the door to manipulation, misinformation, and digital disillusionment.
Advertisement

Know how AI-powered advertising enhances personalized ads, improving engagement, ROI, and user experience in the digital world

Explore how IBM's open-source AI strategy empowers businesses with scalable, secure, innovative, and flexible AI solutions.

Many organizations still lag in adopting AI due to reluctant leadership, fear of unexpected outcomes, and lack of expertise

Knime enhances its analytics suite with new AI governance tools for secure, transparent, and responsible data-driven decisions
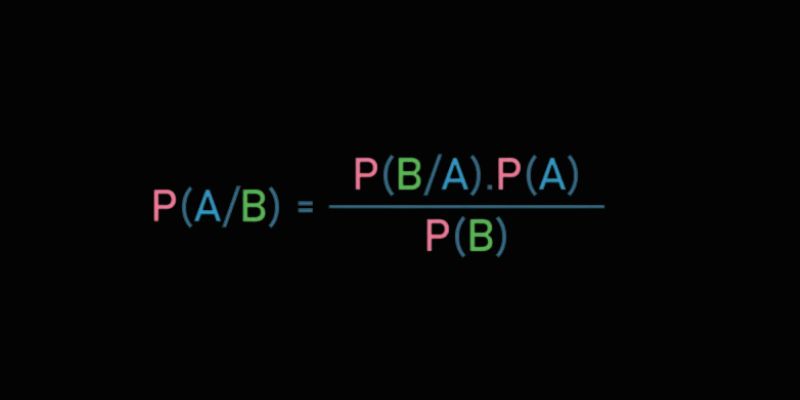
Learn Bayes' Theorem and how it powers machine learning by updating predictions with conditional probability and data insights

Can ChatGPT replace a doctor? Learn why relying on AI for medical advice can lead to dangerous oversights, missed symptoms, and biased answers

Curious about LPU vs. GPU? Learn the real differences between a Language Processing Unit and a GPU, including design, speed, power use, and how each performs in AI tasks

Learn how to create the perfect headshot using LightX Photo Editor. This step-by-step guide covers lighting, background edits, retouching, and exporting for a professional finish

Wondering if third-party ChatGPT apps are safe? Learn about potential risks like data privacy issues, malicious software, and how to assess app security before use

Nexla's Nvidia NIM integration allows scalable AI data pipelines and automated model deployment, boosting enterprise AI workflows

Explore the various ways to access ChatGPT on your mobile, desktop, and through third-party integrations. Learn how to use this powerful tool no matter where you are or what device you’re using
Explore the key differences between class and instance attributes in Python. Understand how each works, when to use them, and how they affect your Python classes