Advertisement
When people talk about large language models (LLMs) today, it usually comes down to a few big names. Google’s Bard, OpenAI’s ChatGPT, and the locally running Alpaca model have each carved out a space. But while they might all serve a similar purpose—generating text based on prompts—the experience you get with each is different. Understanding those differences can help you figure out which one fits your needs better.
Let’s start with what really matters to most users: how well these models respond.
ChatGPT (especially in its GPT-4 version) is known for producing clean, natural-sounding responses that feel thoughtful and often quite helpful. It’s generally solid at following context, referencing earlier messages, and staying on-topic across long conversations. This consistency makes it the default choice for many who rely on LLMs for writing, coding, studying, or brainstorming.
Bard, powered by Google’s Gemini model, tends to be quicker and more focused on pulling in current data. It connects directly with Google Search, which means it can give real-time info—something ChatGPT can’t do without browsing access. But Bard’s tone can sometimes feel stiff, and its answers may swing between too short and overly technical. You might find it offering references or web snippets, which can be useful but often break the flow.
Offline Alpaca, on the other hand, is a completely different setup. It’s not hosted in the cloud but runs locally on your device. That alone gives it an edge in privacy. But since it’s a smaller model compared to GPT-4 or Gemini, you shouldn’t expect the same fluidity or depth in its answers. Its output is more basic, and it sometimes misunderstands prompts, especially if they’re vague or multi-step.
If you care about speed or just need something reliable without jumping through hoops, accessibility becomes important.
ChatGPT offers apps and a smooth interface on both web and mobile. You can start chatting in seconds. The GPT-4 version is paywalled, but GPT-3.5 is free and still works well for most casual needs. Plus, there’s no setup—just log in and type.

Bard is free and also easy to access, with nothing to install or configure. The response time is fast, sometimes even faster than ChatGPT, since it’s integrated deeply into Google’s infrastructure.
Alpaca, being an offline model, requires technical setup. You’ll need the right hardware and some patience to get it running. It’s not a plug-and-play experience. But once it’s set up, you don’t need an internet connection, and there’s no delay from servers or queues.
So, if you’re looking for speed with no setup, Bard or ChatGPT is the better pick. If you want control, privacy, or offline access, Alpaca is your friend—but be ready for the trade-offs.
This is where the offline model pulls ahead.
Offline Alpaca doesn’t send your prompts anywhere. It doesn’t collect data, track usage, or log your chats. It just runs locally, which makes it the clear choice if you’re dealing with sensitive information or just don’t want your inputs going to big tech servers.
ChatGPT and Bard both involve cloud processing. Your prompts are sent to servers, and while companies promise privacy features and allow you to turn off chat history, you’re still depending on their policies. For casual use, that’s not a big issue. But for business users or anyone dealing with private material, that’s something to think about.
Each model works better in different situations.
ChatGPT is the best overall when you need something that handles nuance and long-form writing. Whether you’re coding, summarizing a complex article, or drafting emails, it holds its ground well. The consistency is part of what makes it reliable. It may not always have the freshest data, but it understands tone, detail, and context better than most.
Bard is strong in situations where real-time data matters. Think of things like checking the latest developments, comparing products, or asking for directions. It can act like a smarter version of search. But it’s not as good at sticking to a writing style or handling subtle instructions. Its answers often feel like a mix between a chatbot and search engine results.

Alpaca is for the technically inclined or those who want a model they can customize. It's not going to beat the others in writing quality, but for light usage or offline environments, especially educational ones, it's useful. If you don't mind a little DIY work and rough edges, it can do the job.
The price tag can often be the deciding factor, especially for regular users.
ChatGPT offers a free version using GPT-3.5, which handles most tasks well. But if you want access to GPT-4, you’ll need to subscribe to the Plus plan. It’s a monthly fee, and while the upgrade brings better performance, casual users might not feel the need to pay.
Bard is entirely free at the moment. There’s no paid tier, no credits, and no restrictions beyond general usage limits. That makes it easy to test, compare, or use regularly without thinking about costs.
Offline Alpaca is free to use, but there’s a hidden cost—your time and your device. You’ll need a computer that can handle the model, and setting it up takes effort. There’s no subscription, though, and once it's running, it’s yours with no extra charges.
So if you’re looking to avoid subscriptions, Bard or Alpaca might work better. But if polished output is a must and you're fine with paying a bit each month, ChatGPT Plus makes sense.
All three models—Bard, ChatGPT, and Alpaca—have clear roles, and none is outright better in every category. ChatGPT is polished, well-rounded, and ideal for most daily needs. Bard is fast and great for quick, up-to-date answers. Alpaca is private and offline-friendly, though more basic. The right one for you depends on what you value most. Whether it’s fluid conversation, fresh info, or full control, each option brings something different to the table.
Advertisement
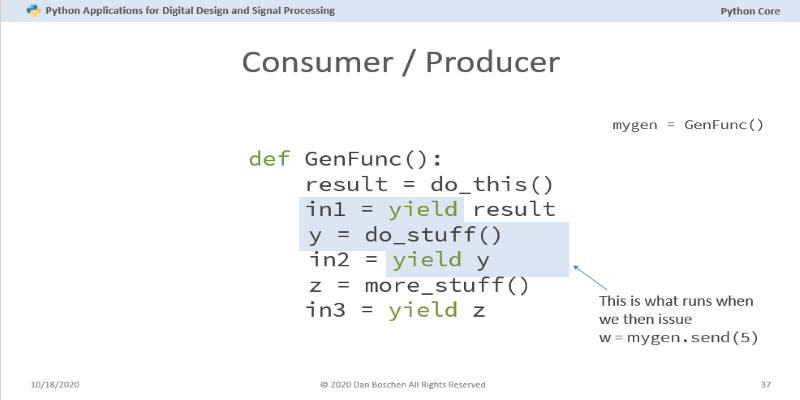
Curious about Python coroutines? Learn how they can improve your code efficiency by pausing tasks and running multiple functions concurrently without blocking
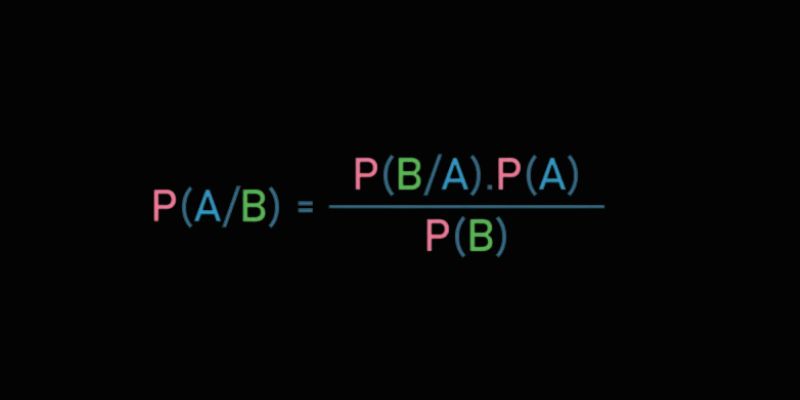
Learn Bayes' Theorem and how it powers machine learning by updating predictions with conditional probability and data insights

Case study: How AI-driven SOC tech reduced alert fatigue, false positives, and response time while improving team performance

Explore how IBM's open-source AI strategy empowers businesses with scalable, secure, innovative, and flexible AI solutions.

Learn why businesses struggle with AIs: including costs, ethics and ROI, and 10 things they can do to maximize output.

Wondering if third-party ChatGPT apps are safe? Learn about potential risks like data privacy issues, malicious software, and how to assess app security before use

Discover 8 powerful ways AI blurs the line between truth and illusion in media, memory, voice, and digital identity.

Ever wanted to make lip sync animations easily? Discover how Gooey AI simplifies the process, letting you create animated videos in minutes with just an image and audio
Think My AI is just a fun add-on? Here's why Snapchat’s chatbot quietly helps with daily planning, quick answers, creativity, and more—right inside your chat feed

Can AI-generated games change how we play and build games? Explore how automation is transforming development, creativity, and player expectations in gaming
Explore the key differences between class and instance attributes in Python. Understand how each works, when to use them, and how they affect your Python classes

Trying to choose between Bard, ChatGPT, and offline Alpaca? See how these language models compare in speed, privacy, accuracy, and real-world use cases